Paul Lebovitz
- Process consulting relative to the integration of user experience design into the product definition and software development process. LeanUX, AgileUX and Agile software development are all a set of principles that must be adapted to the nature of the product, budget, and strengths of the organization .
- User research (Quantitative and Qualitative) relative to both new and existing product and services.
- Definition of interactive LO-FI and HI-FI prototypes
I excel at bringing together people, technology and process to produce products that excite customers, the people building the products, and the financial objectives of the business. I bring a set of skills and experience suitable to building products and services that have strong user experience (UX) and technology components. My skills have been honed at companies including Boeing, Lockheed, Intergraph, Autodesk, and my onging consultancy. My skills are academically founded in my BSME (mechanical engineering) and MSHFID (Human Factors for Information Design) degrees.
During my career I have both worked as an individual UX contributor, UX Architect, Technical Product Manager, as well as led and mentored geographically that have included member from China, Canada, USA, and Europe. I have built and led the product design teams for world class applications including Autodesk’s Inventor and Siemens’ Solid Edge. Additionally, I have led both technical and requirements research for products involving large scale customer engagement.
Designing for User Experience
Total User Experience?
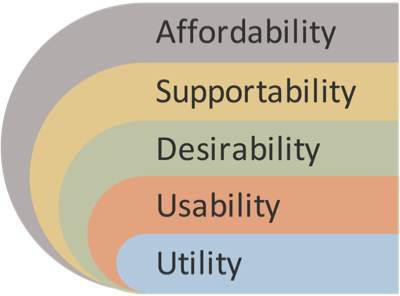
It’s a Team Effort

- Lack of a shared understanding of the business objectives and the assumption on which they are based across the entire product development team.
- There is no a clear understanding of the proposed solution and the minimum viable product by the entire team.
- Barriers to the flow of information, or information not being in an accessible form.
All members of the team leadership must be able to answer questions such as:
- What are the business objectives?
- What is the proposed solution and what are the assumptions on which it is based?
- What is the MVP (Minimum viable product)
- How will the product architecture support the business objectives?
Shared Knowledge is Essential
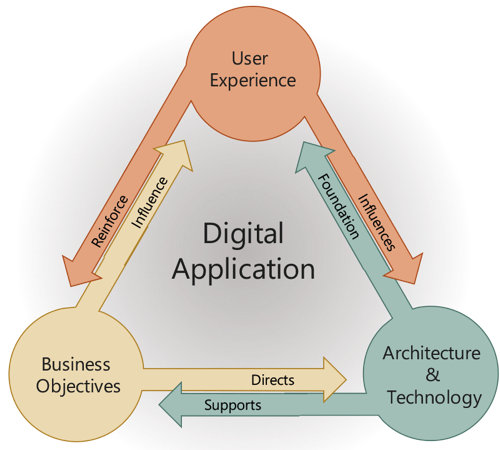
Each organization must support the development of the optimal product using their area of expertise.
User Research - Which Tools to Use
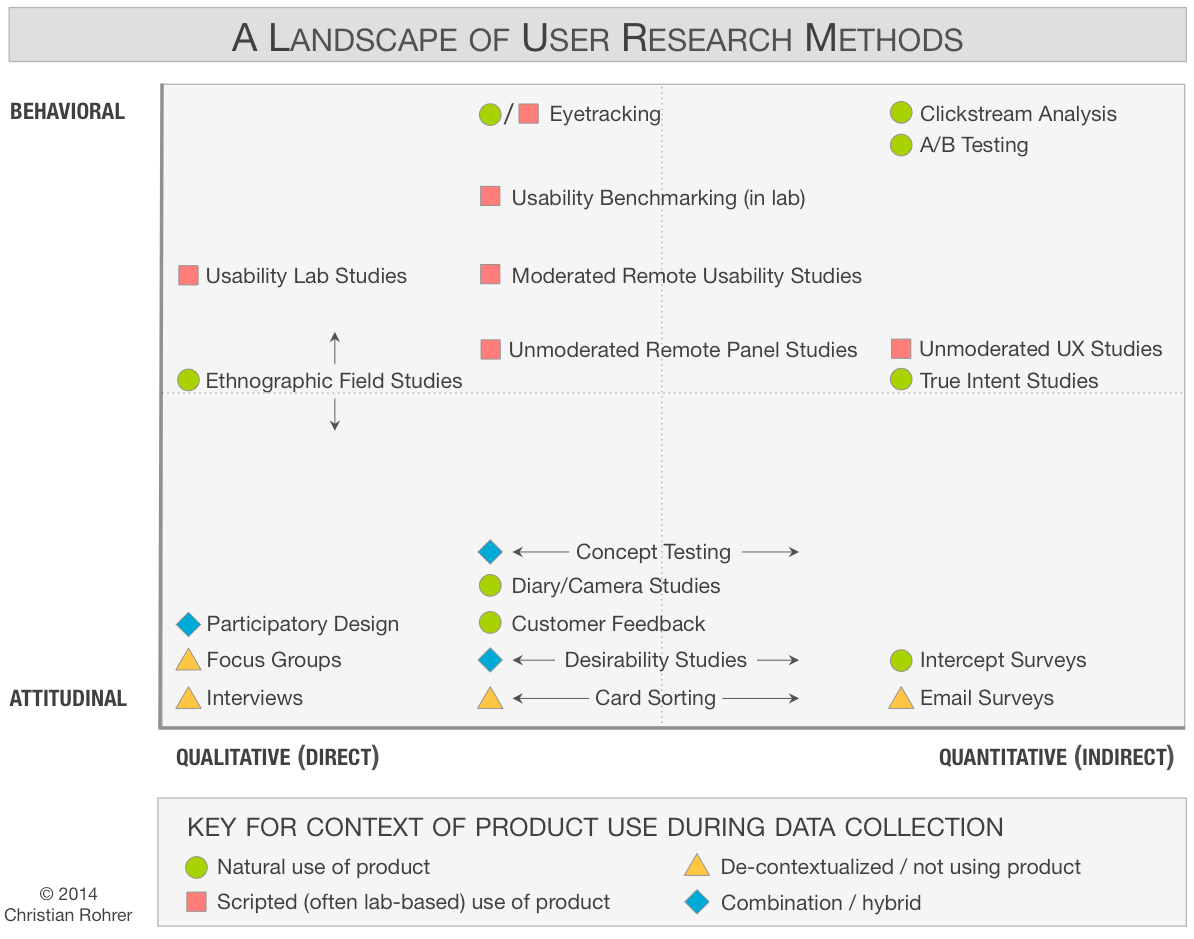
I very much like the classification system proposed by Christian Rohner that presents methods along a 3-dimensional framework with the following axes:
- Attitudinal vs. Behavioral
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Context of Use
Interestingly, advances in machine learning are allowing many qualitative methods to provide quantitate data.
User Experience Design within the Orgranization
Where to Spend Time
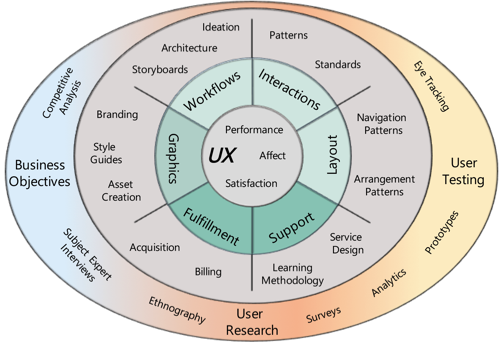
It is important to define the sufficient effort to achieve the TUX objectives. For example, some projects may require no user research while it may be the most important aspect of other projects.
Integrating the User Experience (UX) and Software Development Processes
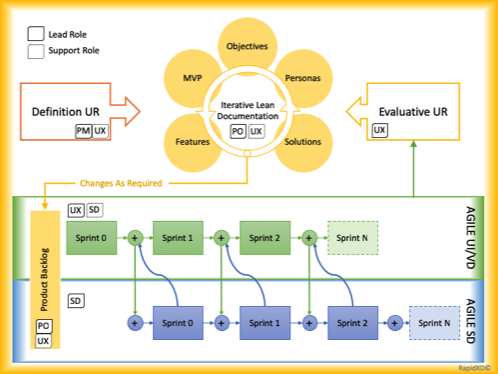
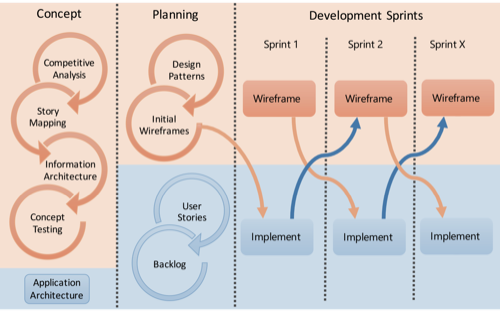
Regardless of the software development process (agile is one example), the two teams need to work within an integrative framework so that the user experience can be evaluated on an ongoing basis.
Product Experience = Affective + Performance
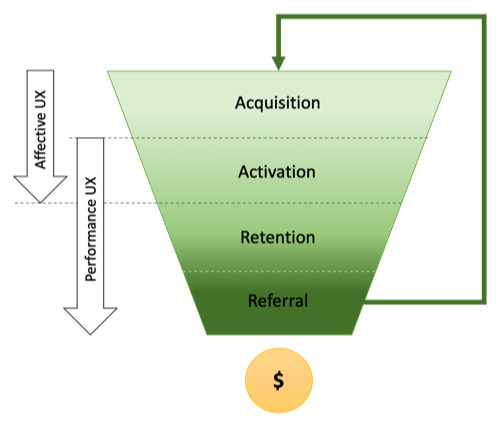
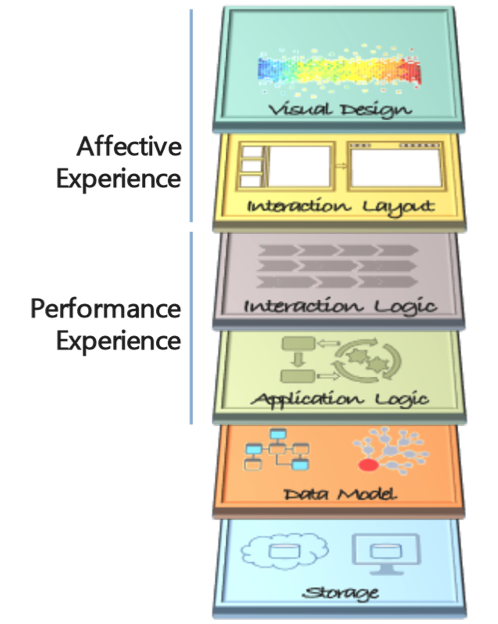
From a product architecture perspective there are six primary components, of which the UX team is primarily responsible for the Visual Design, Interaction Layout, Interaction Logic and Application (business) Logic.
UX Activities and Skillsets
Following are the skill sets (trades) for User Experience
User Research
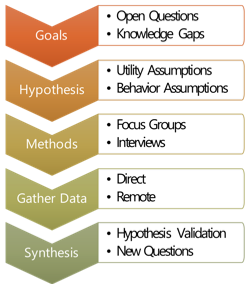
Many different techniques can be employed to gather data. In some cases, simple surveys may be sufficient and in other cases user interviews or focus groups may be needed. Of course product development timelines and budgets are also an important consideration.
I have experience in many methods of user research.
Information Architecture (IA) Design
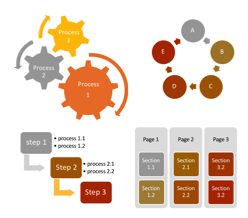
An IA can be very simple in the example of a ‘lookup your weather’ website or extremely complex in the case of a ‘heads-up display’ for a fighter aircraft.
Interaction Design
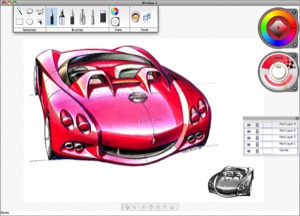
Creating a great user interface requires understanding the target users and applying well-established principles of user cognition – all within a framework of creative exploration.
Often ‘user interaction design’ is confused with ‘visual design’. While great visual design is critical to users’ emotive response, it is the interaction design that guarantees user satisfaction once their interest is captured.
Visual Design

Usability Testing

Depending on the nature of the product and the test scenarios, testing may in some cases be done remotely using video based collaboration tools.
The goal is to identify any usability problems, collect qualitative and quantitative data and determine the participant's satisfaction with the product.
There are two distinctly different scenarios in which User Testing takes place:
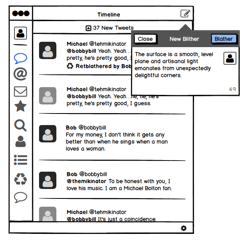
Prototyping
Expert Reviews
Why an Expert Review instead of User Testing?
An expert review is never a replacement for user testing, but user testing can be expensive. It is often possible to get the most out of user testing by first performing an Expert Review that addresses the obvious issues.

